Innovation in Motion: Tapered Roller Bearings Demystified
Introduction: The Role of Innovation in Bearing Technology
Innovation is the driving force behind advancements in bearing technology, shaping the way motion and performance are optimized across diverse industries. At the heart of this innovation lies Tapered Roller Bearings (TRBs), pivotal components that play a crucial role in enabling smooth and efficient motion control in machinery and mechanical systems. we embark on a journey to demystify TRBs, exploring their definition, significance, and the transformative impact they have on industrial operations worldwide.
Defining Tapered Roller Bearings (TRBs)
Tapered Roller Bearings (TRBs) are precision-engineered components designed to facilitate rotational motion by transmitting radial and axial loads along the axis of rotation. Unlike traditional ball bearings or cylindrical roller bearings, TRBs feature tapered rollers and raceways, allowing them to handle both radial and axial loads with precision and efficiency. This unique design characteristic makes TRBs particularly well-suited for applications where heavy loads, high speeds, and precise motion control are required.
Significance of TRBs in Industrial Applications
The significance of TRBs in industrial applications cannot be overstated. From automotive and aerospace to heavy machinery and power generation, TRBs play a pivotal role in ensuring the smooth operation of various mechanical systems. Their ability to withstand high radial and axial loads, accommodate misalignment, and operate at elevated speeds makes them indispensable in critical applications where reliability, durability, and performance are paramount.
Impact of Innovation on TRB Technology
Innovation continues to drive advancements in TRB technology, leading to the development of new materials, manufacturing processes, and design enhancements. From advanced surface coatings to precision-machined components, each innovation contributes to improving the performance, longevity, and reliability of TRBs in demanding operating conditions. By harnessing the latest innovations in TRB technology, engineers and designers can push the boundaries of motion control, unlocking new possibilities for efficiency, productivity, and performance across industries.
In conclusion, Tapered Roller Bearings (TRBs) represent a cornerstone of modern bearing technology, embodying the principles of innovation, precision, and reliability. By understanding the definition, significance, and transformative impact of TRBs, engineers and industry professionals can leverage these versatile components to optimize motion and performance in a wide range of industrial applications.
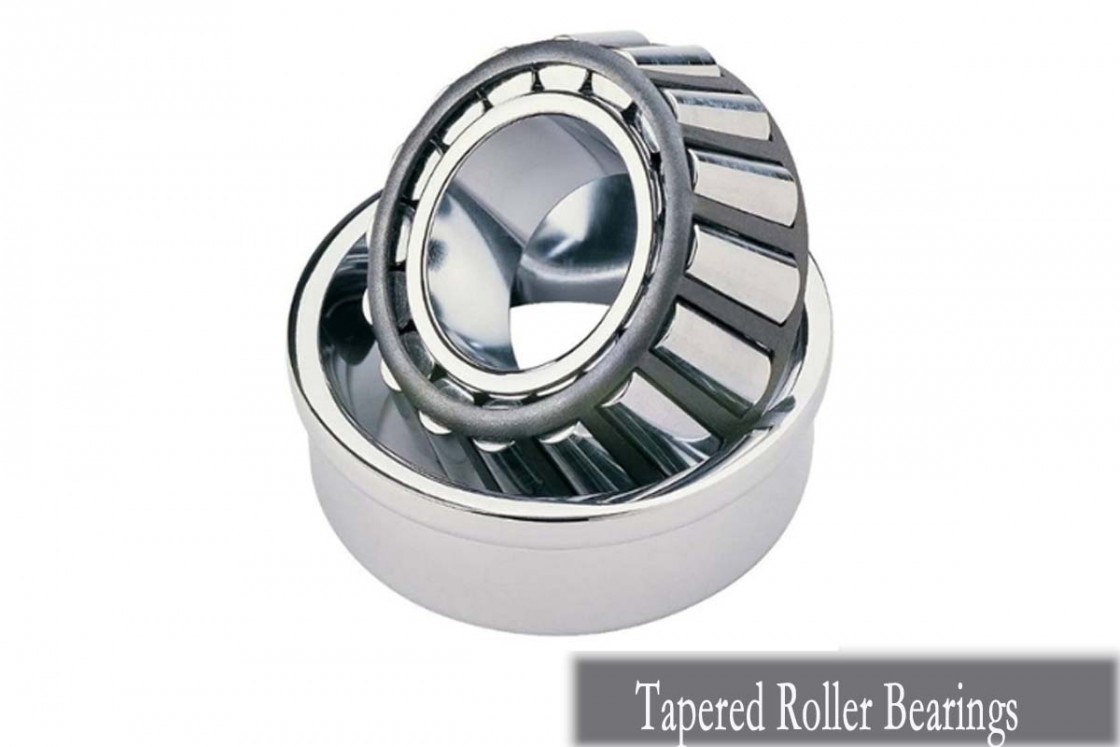

Understanding Tapered Roller Bearings
Tapered Roller Bearings (TRBs) represent a critical component in the realm of bearing technology, renowned for their ability to handle radial and axial loads with precision and efficiency. we delve into the intricacies of TRBs, offering a comprehensive understanding of their structure, functionality, and key terminology.
|
Component |
Description |
|
Inner and Outer Rings |
Provide structural support and guidance for the tapered rollers, allowing them to transmit loads along the axis of rotation. |
|
Tapered Rollers |
Feature tapered profiles, enabling them to accommodate both radial and axial loads efficiently. |
|
Cages |
Maintain the position of tapered rollers and facilitate smooth rotation. |
|
Raceways |
Located on the inner and outer rings, providing the contact surfaces for the rollers, ensuring efficient load transmission and reduced friction. |
|
Comparison with Other Types |
TRBs are uniquely designed to handle both radial and axial loads simultaneously, making them versatile for variable load directions and misalignment. |
|
Key Terminology |
Concepts such as cone and cup assembly, which refers to the arrangement of the inner and outer rings and tapered rollers, and bearing preload, essential for proper installation and maintenance. |
In summary, Tapered Roller Bearings (TRBs) stand as a testament to innovation in motion control technology, offering unparalleled performance and versatility in handling radial and axial loads. By comprehending the structure, functionality, and key terminology of TRBs, engineers and industry professionals can harness their potential to optimize machinery performance and efficiency across diverse applications.
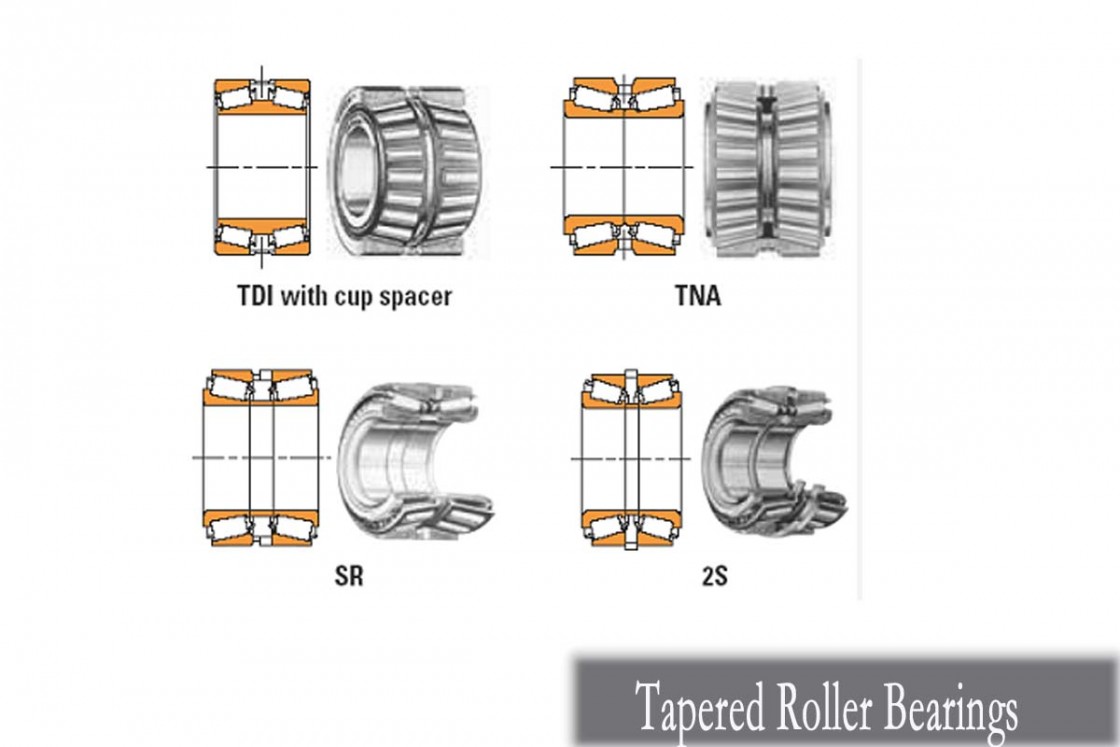
Anatomy and Design Features of Tapered Roller Bearings
Tapered Roller Bearings (TRBs) represent a cornerstone in the realm of bearing technology, offering unparalleled performance and reliability across a wide range of applications. we delve into the intricate anatomy and design features of TRBs, shedding light on their unique attributes and functionalities.
Tapered Shape of Rollers and Raceways
At the heart of Tapered Roller Bearings lies their distinctive tapered shape, which sets them apart from other bearing types. The tapered profile of both the rollers and raceways allows TRBs to efficiently distribute radial and axial loads while maintaining proper alignment. This unique geometry ensures optimal contact between the rollers and raceways, minimizing stress concentrations and promoting uniform load distribution. As a result, TRBs excel in applications where both radial and axial loads are present, delivering exceptional performance and longevity.
Cage Designs and Materials
Another critical aspect of TRB design is the construction of cages, which play a crucial role in guiding the movement of the tapered rollers. These cages are meticulously engineered to provide sufficient clearance for the rollers while preventing excessive contact and friction. Various materials, including steel, brass, and synthetic polymers, are utilized in cage construction to meet specific application requirements. By selecting the appropriate cage design and material, engineers can ensure smooth operation and prolonged service life of TRBs in diverse operating conditions.
Significance of Preload Adjustment and Bearing Clearance
Proper preload adjustment and bearing clearance are paramount to optimizing the performance and longevity of Tapered Roller Bearings. Preload adjustment involves applying a controlled axial load to the bearings to eliminate internal clearances and enhance stiffness. This process ensures that the rollers are in constant contact with the raceways, minimizing backlash and maximizing load-carrying capacity. Additionally, maintaining the correct bearing clearance is essential for preventing excessive friction and wear, thereby extending the operational lifespan of TRBs.
In conclusion, the anatomy and design features of Tapered Roller Bearings (TRBs) underscore their status as a cornerstone of modern motion control technology. By leveraging their tapered shape, meticulously engineered cages, and precise preload adjustment, TRBs offer unparalleled performance, reliability, and versatility across a myriad of industrial applications.
|
Brand |
Features |
Applications |
Notable Products |
|
SKF |
- Advanced design and manufacturing techniques for enhanced performance and reliability. Wide range of sizes and configurations. High-quality materials and precision engineering. Innovative sealing solutions for improved protection. |
Automotive, industrial machinery, aerospace, railway, and marine applications.<br>Used in wheel hubs, gearboxes, transmissions, and axles. |
SKF Explorer tapered roller bearings, SKF Energy Efficient (E2) tapered roller bearings, SKF Xtra Power (X) tapered roller bearings. |
|
FAG |
- Precision engineering and stringent quality control standards. Diverse product range to meet various application requirements. High load-carrying capacity and long service life. Specialized coatings for enhanced durability. |
Automotive, heavy machinery, wind turbines, mining equipment, and construction machinery.<br>Commonly used in wheel bearings and gearboxes. |
FAG Generation C tapered roller bearings, FAG tapered roller bearing units, FAG SmartCheck monitoring system. |
|
Timken |
- Extensive experience and expertise in tapered roller bearing technology. Broad range of products for diverse applications. Enhanced sealing solutions for extended bearing life. Customized designs and engineering support available. |
Automotive, aerospace, agriculture, construction, and industrial machinery.<br>Utilized in wheel bearings, transmissions, and gearboxes. |
Timken SET series tapered roller bearings, Timken MileMate matched wheel bearing sets, Timken Housed Unit tapered roller bearing assemblies. |
|
NSK |
- High-performance materials and advanced manufacturing processes. Optimized internal geometry for reduced friction and heat generation. Sealed and greased options for maintenance-free operation. Customizable designs to meet specific requirements. |
Automotive, industrial machinery, mining, and construction equipment.<br>Applied in wheel bearings, transmissions, and differential assemblies. |
NSK HR series tapered roller bearings, NSK Taper Roller Bearing Units (TRBUs), NSK Integral Shaft Bearing Units (ISBUs). |
|
NTN |
- Robust construction and high-quality materials for reliable performance. Precision engineering for optimal load distribution and durability. Grease-lubricated and sealed designs for low maintenance. Application-specific designs and customization. |
Automotive, heavy machinery, agriculture, construction, and mining applications.<br>Used in gearboxes, wheel hubs, and conveyor systems. |
NTN 4T series tapered roller bearings, NTN Tapered Roller Bearing Units (TRBUs), NTN ULTAGE tapered roller bearings. |
This table outlines the distinguishing features, applications, and notable products of different brands offering Tapered Roller Bearings.
Applications and Performance Characteristics of Tapered Roller Bearings
Tapered Roller Bearings (TRBs) find widespread applications across various industries and machinery, owing to their versatile design and exceptional performance characteristics. Let's delve deeper into the applications and performance aspects of TRBs.
Industries and Machinery Utilizing TRBs:
TRBs are integral components in numerous industries and machinery, where they play a crucial role in ensuring efficient operation and reliability. Some key sectors and applications include:
- Automotive: TRBs are extensively used in automotive applications, including wheel hubs, transmissions, differential assemblies, and steering systems. Their ability to handle both radial and axial loads makes them ideal for supporting vehicle weight and transmitting power efficiently.
- Aerospace: In the aerospace industry, TRBs are employed in aircraft engines, landing gear systems, and flight control mechanisms. Their high load-carrying capacity, precision performance, and reliability are essential for ensuring safe and smooth aircraft operation.
- Heavy Machinery: TRBs are indispensable in heavy machinery such as construction equipment, mining machinery, and agricultural machinery. They withstand heavy loads, shock loads, and harsh operating environments, contributing to the durability and longevity of the equipment.
Performance Characteristics of TRBs:
TRBs exhibit several performance characteristics that make them preferred choices in demanding applications. These characteristics include:
- Load Capacity: TRBs are capable of supporting both radial and axial loads simultaneously, thanks to their tapered design. This capability enables them to handle dynamic and static loads efficiently, ensuring stable and reliable operation.
- Speed and Temperature Resistance: TRBs are engineered to operate at high speeds while maintaining optimal performance. Additionally, they exhibit excellent temperature resistance, withstanding elevated temperatures without compromising performance or durability.
- Load Distribution: TRBs distribute loads evenly across the rolling elements, minimizing stress concentration and extending bearing life. This uniform load distribution results in smoother operation, reduced friction, and lower energy consumption.
Case Studies Highlighting TRB Benefits:
Numerous case studies demonstrate the tangible benefits of utilizing TRBs in various applications. These benefits include:
- Improved Equipment Efficiency: By reducing friction and minimizing power loss, TRBs enhance equipment efficiency, leading to increased productivity and reduced operating costs.
- Friction Reduction: TRBs help mitigate frictional forces within machinery, resulting in smoother operation, reduced wear, and extended component life.
- Minimized Maintenance Requirements: The robust construction and reliability of TRBs translate to reduced maintenance intervals and downtime, resulting in higher equipment availability and improved overall productivity.
In conclusion, Tapered Roller Bearings (TRBs) play a pivotal role across diverse industries and machinery, offering exceptional performance characteristics such as high load capacity, speed, temperature resistance, and uniform load distribution. Their widespread applications and proven benefits underscore their significance in optimizing equipment performance and reliability.
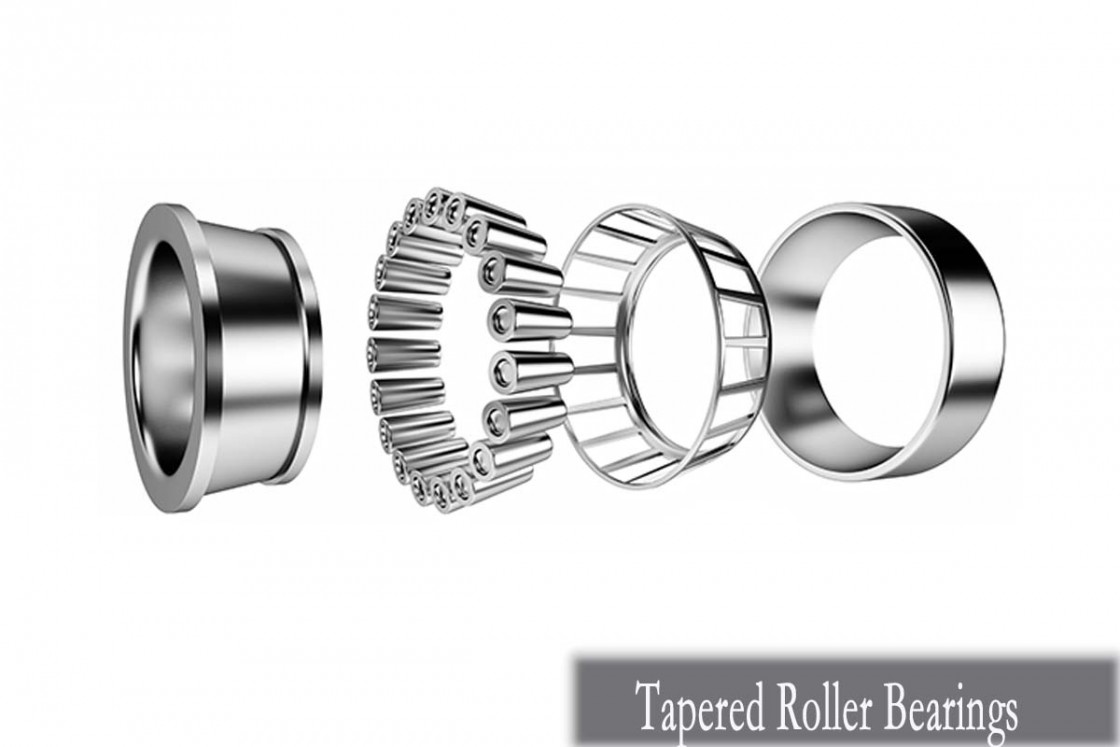

Proper Installation and Maintenance of Tapered Roller Bearings
Tapered Roller Bearings (TRBs) are crucial components in various mechanical systems, and ensuring their proper installation and maintenance is essential for optimal performance and longevity. Let's explore the best practices for TRB installation and maintenance.
Guidelines for Proper TRB Installation:
Shaft and Housing Considerations: Before installing TRBs, it's crucial to inspect the shaft and housing for cleanliness, smoothness, and proper alignment. Any irregularities or contamination can lead to premature bearing failure. Ensure that the shaft and housing dimensions are within tolerance and aligned correctly to prevent excessive loads and misalignment issues.
Preload Adjustment: Proper preload adjustment is vital for optimizing TRB performance. Follow the manufacturer's recommendations for preload values and adjustment procedures. Overly tight or loose preload can lead to premature wear, increased friction, and reduced bearing life. Use precision instruments to achieve the correct preload setting.
Alignment Techniques: Accurate alignment of TRBs is essential for minimizing stress and ensuring smooth operation. Utilize precision alignment tools such as dial indicators or laser alignment systems to align the shaft and housing within specified tolerances. Proper alignment reduces friction, extends bearing life, and prevents premature failure.
Recommendations for Maintenance Practices:
Regular Inspection: Implement a scheduled maintenance program to inspect TRBs for signs of wear, damage, or contamination. Check for abnormal noise, vibration, or temperature rise during operation, as these may indicate bearing issues. Regular inspections allow for early detection of problems and preventive maintenance to avoid costly downtime.
Condition Monitoring: Utilize advanced condition monitoring techniques such as vibration analysis, temperature monitoring, and oil analysis to assess TRB health and detect potential problems. Implement predictive maintenance strategies based on monitoring data to address issues before they escalate into major failures. Regular monitoring enhances equipment reliability and minimizes unplanned downtime.
Lubrication Optimization: Selecting the right lubricants and lubrication methods is critical for maximizing TRB performance and extending service life. Choose lubricants that are compatible with TRB materials and operating conditions. Ensure proper lubrication methods, including the correct quantity and frequency of lubricant replenishment. Proper lubrication reduces friction, prevents corrosion, and maintains bearing integrity.
Conclusion:
Proper installation and maintenance practices are essential for optimizing the performance and lifespan of Tapered Roller Bearings (TRBs). By following guidelines for installation, conducting regular inspections, and implementing effective maintenance schedules, equipment operators can ensure smooth operation, minimize downtime, and maximize the reliability of their machinery. Additionally, selecting the right lubricants and lubrication methods further enhances TRB performance and extends service life, contributing to overall efficiency and productivity.
Recent Advancements in Tapered Roller Bearings (TRBs)
In recent years, significant strides have been made in the field of Tapered Roller Bearings (TRBs), driven by the demand for higher performance, increased reliability, and enhanced durability in various industrial applications. Let's delve into the latest advancements and innovations in TRB technology.
|
Improved Materials |
One of the key advancements in TRB technology is the development of advanced materials with superior mechanical properties and enhanced wear resistance. Manufacturers have been exploring the use of high-strength alloys, advanced ceramics, and specialized coatings to improve the performance and longevity of TRBs in demanding operating environments. These innovative materials offer higher load-carrying capacity, reduced friction, and extended service life, making them ideal for critical applications where reliability is paramount. |
|
Enhanced Coatings |
Coatings play a crucial role in protecting TRBs from corrosion, wear, and surface damage, thereby extending their service life and performance. Recent innovations in coating technology have led to the development of advanced surface treatments, such as diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings, ceramic coatings, and nano-coatings. These coatings offer superior lubricity, corrosion resistance, and anti-wear properties, resulting in smoother operation, reduced maintenance requirements, and improved reliability of TRBs in harsh operating conditions. |
|
Sealing Solutions |
Effective sealing is essential for preventing contamination and retaining lubrication in TRB applications, especially in environments exposed to dust, moisture, and other contaminants. Recent advancements in sealing solutions have focused on developing innovative seal designs, materials, and manufacturing techniques to enhance sealing performance and reliability. Integrated labyrinth seals, triple-lip seals, and advanced elastomeric materials are being employed to achieve superior sealing effectiveness, minimizing the risk of premature failure and enhancing the longevity of TRBs in challenging environments. |
|
Integration of Sensor Technology |
A significant trend in TRB technology is the integration of sensor technology for real-time condition monitoring and predictive maintenance. Sensors embedded within TRBs can continuously monitor key parameters such as temperature, vibration, and bearing condition, providing valuable insights into the health and performance of the bearings. This enables proactive maintenance interventions, such as lubrication optimization, alignment adjustments, and early detection of potential issues, thereby minimizing downtime, reducing maintenance costs, and extending the service life of TRBs. |
|
Future Developments |
Looking ahead, the future of TRB technology holds promising opportunities for further advancements and innovations. Emerging trends such as the utilization of artificial intelligence (AI) for predictive analytics, the development of self-diagnostic bearings, and the integration of smart lubrication systems are poised to revolutionize the field of TRB technology. These future developments aim to further enhance the precision, performance, and durability of TRBs, meeting the evolving demands of modern industrial applications and driving continued innovation in the field. |
Conclusion: Leveraging Innovation with Tapered Roller Bearings
In conclusion, the journey through the world of Tapered Roller Bearings (TRBs) has unveiled a realm of innovation and possibilities, revolutionizing motion systems across various industries.
Anatomy and Design: Through our exploration, we've gained a deeper understanding of the intricate anatomy and design features of TRBs. From the tapered shape of the rollers and raceways to the role of cages in ensuring proper roller guidance, each component contributes to the exceptional performance and reliability of TRBs. By grasping the nuances of their structure, we can appreciate their ability to handle both radial and axial loads with precision, setting them apart as versatile and indispensable components in motion systems.
Applications and Performance: TRBs find extensive applications across a diverse range of industries, from automotive and aerospace to heavy machinery and industrial equipment. Their ability to withstand varying operating conditions, including speed, temperature, and load distribution, makes them indispensable in demanding environments where reliability is paramount. Through case studies, we've witnessed firsthand the tangible benefits of TRBs in improving equipment efficiency, reducing friction, and minimizing maintenance requirements, driving productivity and profitability for businesses.
Driving Innovation: As we conclude our exploration, it's evident that TRBs play a critical role in achieving innovation in motion systems. Their advanced design, coupled with continuous advancements in materials, coatings, and sealing solutions, has propelled the evolution of motion technology to new heights. We stand at the threshold of a future filled with exciting possibilities, where the integration of sensor technology and predictive maintenance holds the promise of even greater efficiency and reliability in motion systems.
Call to Action: In light of these insights, it is imperative for industry professionals to embrace and leverage TRB technology to drive innovation and optimize motion systems. By staying abreast of the latest developments and embracing a culture of continuous improvement, we can unlock new opportunities for efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness. Let us join hands in harnessing the power of TRBs to propel our industries forward, ushering in a new era of innovation and excellence in motion technology.
Innovation in motion begins with Tapered Roller Bearings, and the possibilities are limitless. shaping the future of motion systems with ingenuity, creativity, and a relentless pursuit of excellence.
FAQs: Common Questions About Tapered Roller Bearings
What are Tapered Roller Bearings (TRBs)?
Tapered Roller Bearings, commonly abbreviated as TRBs, are a type of rolling element bearing designed to support both radial and axial loads. They are characterized by their tapered rollers and raceways, which enable them to handle varying load conditions with precision and efficiency.
How do Tapered Roller Bearings differ from other types of bearings?
Unlike ball bearings or cylindrical roller bearings, which primarily support radial loads, TRBs are engineered to accommodate both radial and axial loads simultaneously. This versatility makes them suitable for applications where the load direction fluctuates or is predominantly axial.
What are the key components of Tapered Roller Bearings?
TRBs consist of several essential components, including inner and outer rings, tapered rollers, cages, and raceways. The tapered shape of the rollers and raceways allows for efficient load distribution and alignment, while cages maintain roller spacing and facilitate smooth rotation.
What are the typical applications of Tapered Roller Bearings?
Tapered Roller Bearings find widespread use in various industries and machinery, including automotive, aerospace, heavy machinery, and industrial equipment. They are commonly employed in wheel hubs, transmissions, gearboxes, and axle systems, where reliable performance under diverse operating conditions is essential.
How do you install and maintain Tapered Roller Bearings for optimal performance?
Proper installation and maintenance practices are crucial for maximizing the lifespan and performance of TRBs. This includes ensuring correct shaft and housing considerations, preload adjustment, alignment techniques, and implementing regular maintenance schedules to monitor bearing condition and lubrication.
What advancements have been made in Tapered Roller Bearing technology?
Recent advancements in TRB technology include improvements in materials, coatings, and sealing solutions aimed at enhancing performance, reliability, and longevity. Emerging trends such as sensor integration for condition monitoring and predictive maintenance further contribute to optimizing TRB performance.
How do Tapered Roller Bearings contribute to innovation in motion systems?
TRBs play a critical role in driving innovation in motion systems by providing robust and efficient bearing solutions for various applications. Their ability to handle both radial and axial loads, coupled with continuous technological advancements, makes them indispensable components in optimizing equipment performance and reliability.
These common questions provide valuable insights into the functionality, applications, and advancements in Tapered Roller Bearings, demystifying their role in motion systems and highlighting their significance in various industries.